Trading Strategies Involving options
- If a portfolio consists of a long position in a stock plus a short position in a call option, then this is known as writing a covered call. The long stock position covers or protects the investor from payoff on the short call that becomes necessary if there is a sharp rise in the stock price.
- A spread trading strategy involves taking a position in two or more options of the same type (i.e., two or more calls or two or more puts).
Bull Spreads
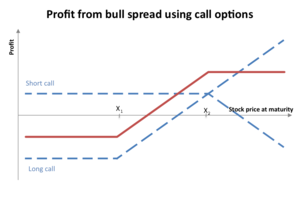
Image courtesy: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/06/Bull_spread_using_calls.png/300px-Bull_spread_using_calls.png
The above diagram represents what the profit function of a Bull spread looks like.
- One can construct a bull spread using Call options.
- Long a call option with strike price \(K_2\),
- Short a call option with strike price \(K1 < K_2\). (Note: Since \(K_1<K_2\), \(C_E(K_1)>C_E(K_2)\).
- The Bull spread strategy limits the investors upside as well as downside risk.
- One can also construct the bull spread using two put options in a similar way.
- An investor who enters into a bull spread is hoping that the stock price will increase.
Bear Spreads

Image courtesy: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/0f/Bear_spread_using_puts.png
The above diagram represents the profit function of a Bear spread.
- An investor who enters into a bear spread is hoping that the stock price will decrease.
- One can construct a bear spread using two put options
- Long a put option with strike price \(K_2\)
- Short a call option with strike price \(K_1<K_2\). (Note: Since \(K_2<K_2\), \(P_E(K_1)<P_E(K_2)\))
Box spread
- Box spread is a combination of bull call spread with strike price \(K_1\) and \(K_2\) and bear call spread with the same strike prices. The payoff of a box spread is always going to be \(K_2 - K_1\).
Butterfly spreads
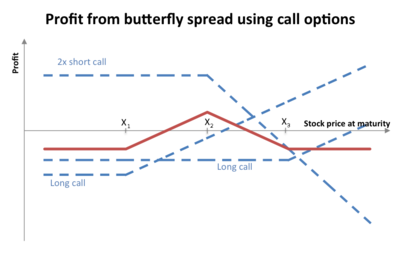
Image courtesy: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/5/52/Butterfly_spread_with_calls.png/400px-Butterfly_spread_with_calls.png
The above diagram represents the profit function in a Butterfly spread.
- A butterfly spread involves positions of options in three different strike prices.
- The butterfly spread can be modelled with the help of following strategy
- A long call option at strike price \(K_1\)
- Two short call option at strike price \(K_1 < K_2\)
- A long call option at strike price \(K_3\) (Note: Since \(K_1 < K_2 < K_3\), \(C_E(K_1)>C_E(K_2)>C_E(K_3)\), also one may choose \(K_2 = (K_1+K_3)/2\))
- The butterfly spread is usually used when the investor thinks that the stock price is going to be relatively stable.
Note: Using the put call parity, one can easily convert spreads modelled via calls into puts and vice-versa.
References. Chapter 10, Trading strategies involving options, Options futures and other derivatives 7ed; John C. Hull.